Routing and Order Cascades in Financial Streams
Introduction
Efficient financial transaction processing is crucial for businesses handling multiple payment methods and providers. Properly configured routing and cascading mechanisms ensure higher success rates, reduced transaction costs, and optimal performance. As the complexity of financial transactions grows, companies must adopt advanced solutions to manage their transaction flows effectively. Businesses that fail to implement structured financial flow management risk facing increased transaction failures, higher operational costs, and unsatisfied customers.
In this article, we will explore the key concepts of financial flow routing and order cascades, explaining their significance and the advanced tools offered by PayStar that enable businesses to streamline their financial operations. By understanding how routing and cascading work, businesses can enhance their payment processing strategies and remain competitive in an evolving financial landscape.
What is Financial Flow Routing?
Financial flow routing refers to the process of directing transactions to specific payment providers based on predefined rules. These rules are designed to optimize transaction efficiency, minimize costs, and enhance security. A well-structured routing system takes various factors into account, such as transaction type, geographical location, provider success rates, and cost efficiency. By carefully analyzing these factors, businesses can make informed decisions about which providers to use for each transaction.
Routing is particularly important for businesses operating in multiple regions. Different payment providers have varying approval rates based on geographic factors, which means that a transaction may have a higher success rate when routed to a local provider rather than an international one. Additionally, some providers may specialize in specific types of transactions, such as high-value transfers or recurring payments. By leveraging intelligent routing, businesses can ensure that each transaction is processed through the most suitable provider, increasing the likelihood of successful payment completion.
What is an Order Cascade?
An order cascade is a sequential process where a transaction is attempted through multiple payment providers in a predetermined order. If the initial provider declines the transaction, it is automatically rerouted to the next available provider in the cascade. This mechanism ensures transaction continuity and reduces the chances of failed payments.
The cascading approach is crucial for businesses that rely on consistent and uninterrupted payment processing. If a primary provider experiences technical issues or temporarily halts processing, the transaction does not need to fail outright. Instead, it moves to an alternative provider, allowing businesses to maintain a high success rate in their payment operations. This strategy is especially beneficial in industries with high transaction volumes, where even a small percentage of failed payments can result in significant revenue losses.
In addition to increasing transaction success rates, order cascades also improve the overall customer experience. Customers expect seamless payment processes, and a failed transaction can lead to frustration and abandoned purchases. By implementing an efficient cascading system, businesses can reduce payment disruptions and provide their customers with a more reliable transaction experience.
Key Differences Between Routing and Cascading
While routing and cascading are related concepts, they serve different purposes in financial transactions. Routing is the initial decision-making process that determines the primary provider for a transaction based on predefined rules. This allows businesses to optimize costs, minimize risks, and maximize transaction efficiency. In contrast, cascading acts as a backup mechanism, ensuring that transactions can still be completed even if the initially selected provider is unavailable or rejects the payment.
Both mechanisms play complementary roles in financial flow management. Routing helps businesses proactively select the best provider, while cascading provides a safety net to prevent transaction failures. By combining these two strategies, businesses can create a highly resilient payment processing system that adapts to changing conditions and minimizes potential losses. Now that we understand the differences, let’s explore practical use cases demonstrating the impact of these strategies on transaction costs and success rates. Now that we understand the differences, let’s explore practical use cases demonstrating the impact of these strategies on transaction costs and success rates.
Practical Examples of Routing and Cascading with Cost Optimization
For businesses, maximizing approval rates is essential, but so is minimizing transaction costs. Instead of prioritizing the provider with the highest success rate, a more cost-effective approach is to start with the cheapest provider and escalate to more expensive ones only if necessary.
Cost-Optimized Cascading Strategy
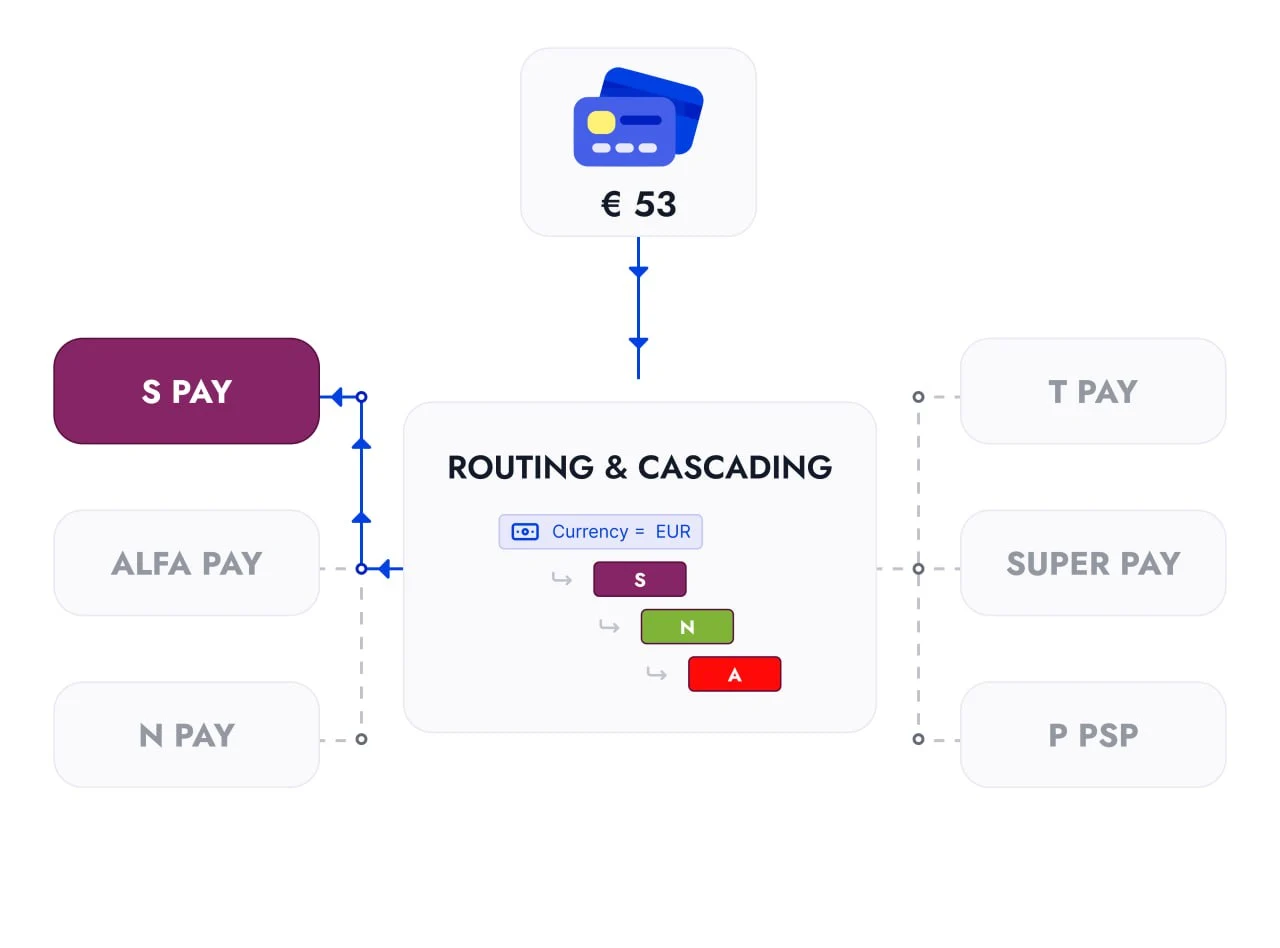
For businesses, maximizing approval rates is essential, but so is minimizing transaction costs. Instead of prioritizing the provider with the highest success rate, a more cost-effective approach is to start with the cheapest provider and escalate to more expensive ones only if necessary.
Provider C: Success rate – 40%, Transaction fee – 1%
Provider B: Success rate – 60%, Transaction fee – 1.7%
Provider A: Success rate – 80%, Transaction fee – 2%
In a cost-first cascading strategy, the transaction is first attempted through Provider C, the cheapest option. If it fails, it moves to Provider B, which has a slightly better success rate but a higher fee. Finally, if B also declines, it is processed by Provider A, which has the highest success rate but also the highest cost.
Cost-Optimized Routing Strategy
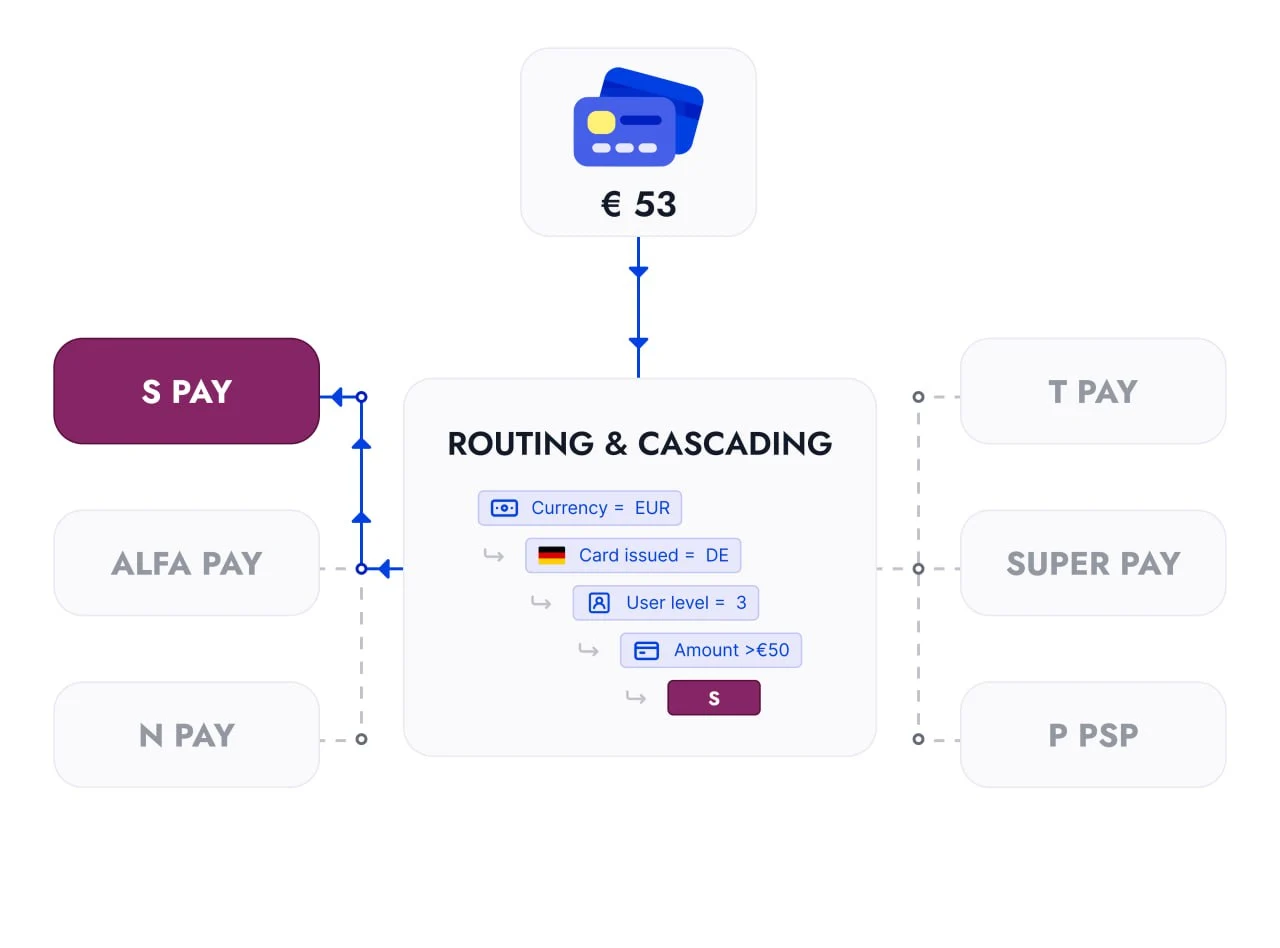
Routing can also be optimized for both cost and conversion rates based on the type of transaction. Here’s an example:
Visa transactions are routed to Provider C as the cheapest option unless it has poor Visa acceptance. MasterCard transactions are routed to Provider B since it offers better conversion for MasterCard at a mid-tier cost. Transactions below $50 are routed to Provider C, as small transactions often succeed with lower-cost providers. Transactions above $50 are routed to Provider A, as larger transactions need a provider with a higher success rate.
Combining Cost-Optimized Routing and Cascading
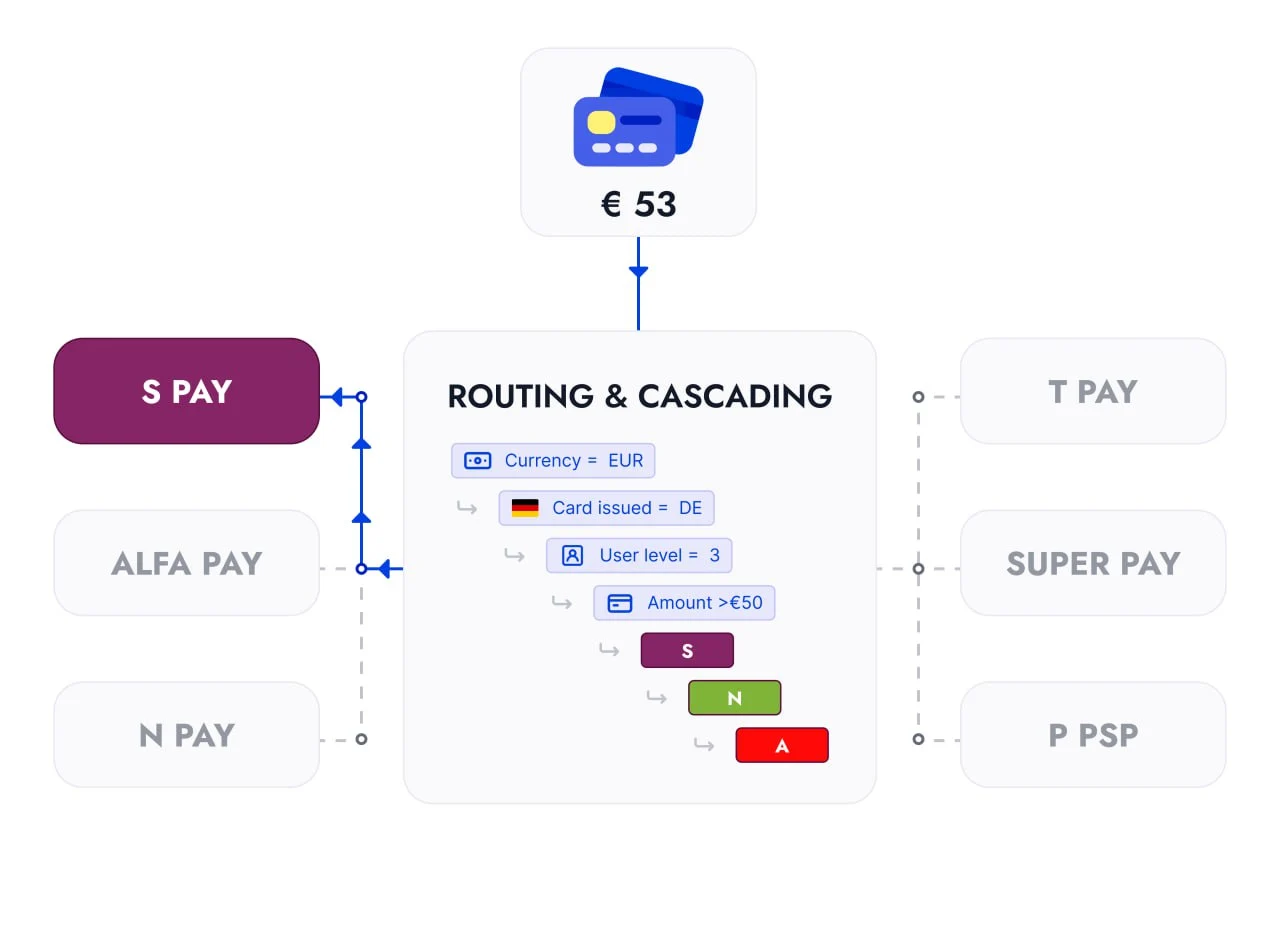
To maximize cost efficiency and approval rates, businesses can implement both routing and cascading together.
Primary Routing (Cost-Based Selection)
Visa transactions are sent to Provider C as the cheapest first choice. MasterCard transactions go to Provider B, which offers a better success rate. Transactions below $50 are routed to Provider C, while transactions above $50 are routed to Provider A.
Cascading as a Fallback (Cost-First Approach)
If Provider C rejects a Visa transaction, it moves to Provider B, then to Provider A. If Provider B rejects a MasterCard transaction, it moves to Provider A. If a transaction below $50 fails with Provider C, it moves to Provider B, then Provider A. If a transaction above $50 fails with Provider A, it moves to Provider B, then Provider C.
This hybrid model ensures that transactions are processed through the cheapest provider first while maintaining a fallback to providers with higher approval rates when needed.
Why is This Important for Businesses?
For businesses handling large volumes of transactions, an optimized financial flow management strategy is crucial. Maximizing transaction approval rates directly impacts revenue and customer satisfaction. If a business frequently experiences transaction failures, it risks losing customers to competitors with more reliable payment systems. By using intelligent routing and cascading mechanisms, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood of payment declines and enhance their reputation for reliability.
Cost optimization is another major benefit of structured routing and cascading. Processing fees vary between payment providers, and businesses can strategically route transactions to the most cost-effective providers without compromising on approval rates. By continually analyzing and adjusting their routing strategies, businesses can reduce operational expenses while maintaining a high success rate.
In addition to financial benefits, routing and cascading contribute to fraud prevention and risk management. Some payment providers have stricter fraud detection measures than others, making them more suitable for handling high-risk transactions. Businesses can incorporate these factors into their routing strategies to balance security and efficiency, ensuring that transactions are both safe and successful.
PayStar's Intuitive Tools for Financial Flow Configuration
PayStar offers a highly intuitive toolset for configuring financial flow routing and cascades. Businesses can leverage these tools to create custom transaction pipelines, assign priority levels to providers, and implement failover strategies to enhance payment reliability. One of the key advantages of PayStar’s system is its ability to provide real-time analytics, allowing businesses to monitor transaction performance and adjust routing rules dynamically.
PayStar’s merchant-specific customization capabilities enable businesses to define unique routing and cascading rules that align with their operational requirements. This flexibility ensures that businesses can tailor their financial flow strategies to optimize transaction success rates and cost efficiency. Additionally, automated failover mechanisms guarantee that transactions are instantly rerouted in case of provider failures, minimizing disruptions and maintaining a seamless payment experience for customers.
Another significant advantage of PayStar’s financial flow management system is its ability to integrate with multiple payment providers simultaneously. Businesses no longer need to rely on a single provider, reducing their exposure to provider-specific downtimes and increasing overall transaction resilience. With PayStar, companies can make data-driven decisions to optimize their payment processing strategies and maintain consistent financial flow efficiency. With PayStar’s advanced configuration tools, businesses can seamlessly implement these routing and cascading strategies, ensuring optimal cost efficiency and transaction reliability. With PayStar’s advanced configuration tools, businesses can seamlessly implement these routing and cascading strategies, ensuring optimal cost efficiency and transaction reliability.
Conclusion
Optimizing financial transactions through intelligent routing and cascading is essential for businesses seeking reliability and cost-efficiency. PayStar’s advanced tools empower companies to take control of their financial flows, ensuring seamless payment processing with minimal disruptions. By implementing these strategies, businesses can reduce transaction failures, optimize costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
As financial transactions continue to evolve, adopting sophisticated routing and cascading mechanisms will be a critical factor in maintaining a competitive edge. Businesses that invest in advanced financial flow management solutions will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of modern payment processing and achieve long-term success.

